Panel discussion on...
Healthy lifestyle
Welcome in the world of alternative meat: analytical challenges and perspectives

Below the surface:
Sustainable marine ingredients
Innovation and motivation in nutritional supplements
Consumers and formulators of nutritional products are hungry for functional ingredients to support healthy ageing. To meet market demand, ingredient suppliers must not only demonstrate their offerings are natural, certified organic and supported by rigorous scientific evidence but are sustainably sourced. In recent years, researchers have turned their attention to the oceans in search of bioactive compounds that tick all these boxes.
Despite the best efforts of scientists, an estimated 90% of marine species remain undescribed (1). Therefore, vast potential exists below the surface to harness biologically active compounds that can support human nutrition. Particular interest exists in macroalgae, commonly known as seaweeds. Not only are seaweeds a nutritious food source, but their unique bioactive constituents are increasingly being utilised in everything from nutraceutical and cosmeceutical products through to biomedical applications and pharmaceutical research.
The seaweed revolution is rapidly gaining momentum. The Global Seaweed Coalition reports that seaweed is the world’s fastest growing food production sector, doubling in size in the 10 years to 2015 (2). The Coalition’s role is to oversee the safety and sustainability of the industry as it aims to scale up and produce 15 times more seaweed by 2050 – a move with the potential to make a significant contribution towards the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals.
Forward-thinking governments, particularly those with vast coastlines at their disposal, are preparing to embrace a future focussed on marine bioproducts. Australia is a prime example, where $270 million is being invested to create and expand a dynamic and sustainable marine biotechnology industry (3).
A 2023 report published by the World Bank summarised new and emerging global markets for seaweed (4). In exploring the commercial opportunities for seaweed applications, the report identified the utilisation of seaweeds, and seaweed extracts, for nutraceuticals as one of the most promising market growth opportunities. The report noted that seaweeds and their bioactive compounds are predicted to fuel a seaweed nutraceutical market of USD $3.9 billion by 2030.
Naturally occurring bioactive constituents of seaweeds, such as polysaccharides, polyphenols and polyunsaturated fatty acids, lie at the heart of this growth. Fuelled by scientific interest and a burgeoning number of published research studies attesting to their various bioactivities, seaweed compounds are capturing the attention of nutritional formulators worldwide.
Fucoidan is an intriguing example. A class of long chain, sulphated polysaccharides, fucoidans are found naturally in brown seaweeds. Serving to protect the seaweed from marine pathogens and challenging environmental conditions, fucoidans also offer a wide range of potential benefits to human health (5). More than 3500 scientific papers have been published on fucoidan, exploring their bioactivity across health targets ranging from immune support and gut health through to healthy ageing (6) (Search technical articles using the keyword ‘fucoidan’). Like any ingredient, quality and efficacy can vary and not all fucoidan extracts are the same. It is essential that formulators perform due diligence to ensure they are sourcing high purity, certified organic fucoidan that not only has global regulatory acceptance but is sustainably sourced and supported by a transparent supply chain to meet consumer demands.
At the pinnacle of the fucoidan industry are biotechnology leaders innovating on this very front. They supply high purity, efficacious fucoidan extracts that adhere to meticulous quality assurance protocols and safety standards, including HACCP, ISO9001 and GMP accreditations. Some have invested significantly in the development of propriety ‘green chemistry’ extraction technologies to avoid the use of solvents that can potentially degrade the bioactivity of the compound. They also demonstrate a traceable supply chain, from sustainable seaweed harvesting through to packaging and delivery.
Seaweed processing operations have increased markedly in the past 20 years. Most of this increase has been fuelled by seaweed farming. Asia accounts for more than 97% of the world’s seaweed production, and 99% of that seaweed is cultured artificially (7).In comparison toother food crops, seaweed cultivation offers a distinct range of advantages. It does not require fresh water, fertilisation requirements are minimal, and the process can have other ecological benefits including as the removal of excess nutrients and carbon dioxide.
Whilst seaweed farming in polluted waters can help to improve water quality and restore marine ecosystems, the ability of seaweed to absorb heavy metals and other toxins means formulators should proceed with caution. The quality of the source seaweed has a direct influence on the quality of the bioactive compounds contained within it.
For this reason, a number of companies harvesting seaweed, including leading fucoidan producers, choose to focus on wild seaweeds sourced from remote locations. Sourcing well away from potential sources of industrial, human or agricultural contamination ensures seaweeds of unparalleled quality. The sustainable hand-harvesting of wild seaweeds occurs in several countries with remote coastlines, including Argentina, Canada, Scotland, Australia and Norway. Seaweed is a rapidly renewable resource, and wild stocks have been successfully managed by these nations for decades. Some countries are also harvesting invasive seaweed species – not only supporting human health but simultaneously supporting biodiversity in their native marine environments.
Sustainability practices will remain a key element in the future growth of the global seaweed industry. New product formulators can take heed that leading the charge are innovative ingredient suppliers who have already established clear alignment with the Sustainable Development Goals, whilst simultaneously forging biotechnology pathways for the betterment of human health.
Sustainable sourcing
For example, our MenaQ7 Vitamin K2 as MK-7 is recognized for being clinically validated for bone health in children (1) and adults (2), and for cardiovascular health in adults (3,4). Last year, we introduced our new Palm-Free MCT Oil, which exemplifies our commitment to sustainability and quality. Our organically certified MCT Oil is derived exclusively from coconut sources. By making this conscious choice, we ensure we offer a more sustainable solution without compromising quality.
Sustainable processes
Another example is our newest ingredient offering, crafted by fermentation specifically to protect the native Rhodiola botanical species.
Found naturally in high altitudes in Europe and Asia and taking over 20 years to mature, the increasing demand for Rhodiola rosea became the main threat of overharvesting it. To ensure its sustainable harvest and trade, Rhodiola species were added to the CITES list of endangered species. Consequently, developing ecological ways to harness the benefits of Rhodiola has become a key step in preserving this species.
But we can still enjoy the benefits of this miraculous plant through an innovation in manufacturing: our fermentation process bypasses the need to harvest Rhodiola rosea, becoming CITES compliant by design.
Sustainable facilities
Finally, this commitment extends from our production processes to our facilities. Spawning from a desire to re-industrialize the Hainaut region in Northern France and a citizen commitment to rehabilitating a former industrial wasteland (Usinor), the upcoming Denain greenfield plant will create more than 100 jobs.
Our Denain plant will produce Gnosis's chondroitin, which will be unlike anything else currently available. Chondroitin is a recognized solution for reducing joint pain; however, 80% of the chondroitin in the market is manufactured in China, and 100% is produced from animal cartilage. Gnosis's Chondroitin will be produced using a natural fermentation process that is sustainable (bio-sourced in compliance with biodiversity), non-animal, and efficient (high purity and bioavailability).
The choice of the site is in line with the company's commitment: a desire not to artificially develop soils, along with the construction of a diverse 5.9-hectare compensation area for fauna and flora, creation of a 1.2-hectare nature reserve, and construction of habitats for various species.
In closing, human well-being depends on preserving the environment before anything else. This is why we transform microorganisms through natural processes like fermentation, acknowledging the fragility of our planet and striving to preserve it.
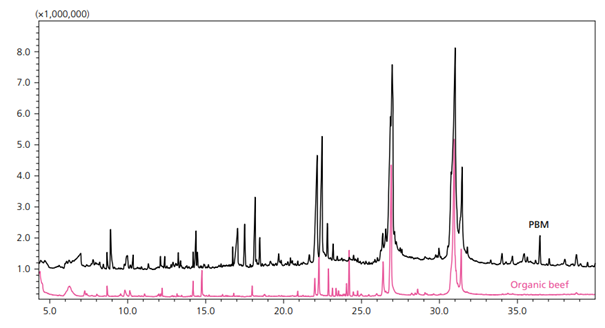
Figure 1. Overlaid Representative Chromatograms for PBM (black) and Organic Beef (pink) (6).
Panelists
References and notes
- Sigwart, D. et al. 2021. Unlocking the potential of marine biodiscovery. Natural Products Reports. 38, 1235-1242. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2021/np/d0np00067a
- www.safeseaweedcoalition.org
- https://mbcrc.com/
- World Bank. 2023. Global Seaweed: New and Emerging Markets Report, 2023. Washington, DC: World Bank. https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/environment/publication/global-seaweed-new-and-emerging-markets-report-2023#:~:text=The%20Global%20Seaweed%20New%20and,potential%20beyond%20its%20current%20markets.
- Fitton, J.H. et al. 2019. Therapies from Fucoidan: New Developments. Marine Drugs.17, 571. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6836154/
- www.scopus.com - Search technical articles using the keyword ‘fucoidan’.
- Zhang, L. et al. 2022. Global seaweed farming and processing in the past 20 years. Food Production Processing and Nutrition 4, 23. https://fppn.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s43014-022-00103-2
Questions
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
How have consumer awareness & demands related to healthy lifestyle changed in the last 12 months?
Where do you see the greatest scientific achievement in nutritional sciences in the last 12 months?
Are there specific health benefit areas in which significant more clinical studies are being done than in others, comparing the last 3 years?
What are the key influencers driving consumer purchasing decision for supplements or health foods? Is substantiation of claims important?
How do consumer today judge their health status?
Please put the following parameter in order 1 highest priority 7 lowest priority:
- Physical Symptoms, like pain, fatigue, constipation, weight gain
- Fitness Levels: endurance, strength, flexibility,
- Health Tracking Devices and heart rate, sleep patterns, steps taken
- Diet and Nutrition: intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins.
- Mental and Emotional Well-being: stress levels, emotional balance, happiness
- Quality of sleep: Sleep quality and duration
- Medical Check-ups: blood pressure checks, cholesterol screenings, blood sugar tests
6.
Delivery formats can support consumer compliance and underline the technology driven approach of the brand.
a.
b.
c.
Do you see a consumer trend in preferences for certain delivery formats?
Are delivery format preference a regional, cultural aspect like taste?
Do you see a trend to carry out ingredient clinical trials using a selected delivery format as study product formulation or are most clinical studies still done in capsules?
7.
Consumer health concerns can vary widely across different regions and demographics globally. However, several common health concerns tend to be prevalent across various countries and populations due to globalization, lifestyle changes, environmental factors, and access to information.
a.
b.
Which are the key global consumer health concerns?
Do you see regional differences?
8.
There is a significant increase in the availability of apps and digital platforms focused on healthy lifestyle, particularly to support personalized approaches to mental wellbeing, metabolic support, weight management and physical fitness.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Do you see lifestyle apps as competition for supplement brands?
Do you think that these apps help to educate consumers, being more targeted when searching for supplements?
Did you consider setting up a lifestyle app to promote your supplement or your ingredient?
Did you set up a lifestyle app to promote your supplement/ ingredient and can you explore about your experience and business impact?
9.
AI (Artificial Intelligence) algorithms are today offered for various aspects of clinical trials to proof efficacy of your health ingredient or supplement.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Are consumers looking for substantiation of claims through AI driven clinical trials?
Did you consider working with an CRO specialist in AI to investigate your health ingredient or supplement?
If you applied already AI methods during the discovers/ development of your health ingredient, please share your experience and recommendation with us.
Do you think that in 2030 AI will be a manifest tool for clinical trials?
10.
A healthy lifestyle may also involve a commitment to sustainable practices for both personal and planetary health. This could include supporting ethical and environmentally conscious products.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
Do you agree that sustainability has become a growing concern also in the nutraceutical industry?
Are consumer looking proactively for brands which have ethical and environmental principles?
Are you looking for ethically sourced raw materials, ingredients?
Did you implement measures to establish resource-efficient processes?
Are you developing socially useful products and how do you define it?
11.
What are the major geographical differences related to healthy lifestyle trends?
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
What are the latest trends related to claims and product forms in China?
In the U.S.
In Mexico
How are claims and dosage forms differentiated in Europe? How does your company ensure compliance with health and safety regulations in Europe?
Do you have a country where you would like to speak about trends for products?
12.
Focus clinical studies. Overall, there has been a recognized push for more gender-inclusive, geographical, and target group focused clinical research. The same trend can be seen in clinical trials for supplements or functional foods.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Please select an area you are active in and let us know which is your hot topic ingredients for 2024 for this area, based on substantiated claim, parameters, biomarkers being studied and/ or clinical study being done. Please name ingredients by scientific name and composition and not by brand name.
Please select your geographical area:
Western (EU, USA)
Asia (China, Japan, Asia Pacific)
Americas (Middle and Latin America)
Kids development/ early life nutrition/infant in Western countries and AP
Adult nutrition and prevention of developing disease
Elderly nutrition and how to support quality of life during aging
Sports nutrition, within different life decades and activity levels
References and notes























