Panel discussion on...
Healthy lifestyle
Welcome in the world of alternative meat: analytical challenges and perspectives

A holistic approach to health: sustainability driving innovation and shaping consumer preferences
Innovation and motivation in nutritional supplements
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines health as a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being (1). A healthy lifestyle is the sum of actions and steps taken to help achieve a healthy state. In 2010, WHO provided a series of recommendations to promote and support healthy lifestyles, like eating lots of fruits and vegetables, reducing fat, sugar and salt intake and exercising (2). Worldwide consumers are nowadays very conscious about their health and, according to a FMCG Guru report, 67% of consumers state that they are making greater efforts to lead a healthier lifestyle (3).
10) Consumers are adopting a holistic approach to wellbeing that also includes environmental considerations. A healthy lifestyle is increasingly linked to sustainability: 68% of consumers associate environmentally friendly diets with being healthier; 49% of consumers report to have made changes to their diets in the last two years to lead a more sustainable lifestyle. Carbon emissions and global warming are the biggest concerns: 64% of global consumers have made changes in their diets and lifestyle in a way to reduce their carbon footprint and 58% of them report to have made great efforts to find sustainably sourced food (3). Certainly, sustainability is and will continue influencing purchasing habits. Companies must address consumers’ concerns by taking actions to reduce the impact of their products and operations on the environment and demonstrate their ability to act as socially responsible corporations.
There are many ways in which a company can adopt a sustainable approach. The naturality of ingredients and raw materials (clean-label, ethically sourced, organically produced), the manufacturing processes (optimized use of energy and water, reduced waste and emissions, upcycling strategies), the packaging (recyclable materials, reduction or replacement of plastic) etc. All the above are different angles to consider when designing, developing, and marketing healthier and more sustainable food products.
In terms of products to offer, the interest in plant-based diets continues to raise. Consumers report to have made changes to cut down or eliminate their consumption of dairy (41% of consumers) and meat products (40% of consumers) (3) and therefore providing alternatives to animal derived products is a way to address this trend. Microbial-derived ingredients are a good solution to fulfill the nutritional needs of vegan and vegetarian consumers. These ingredients can replace or complement animal derivatives and chemical-based products in a variety of nutrition and health applications. In our company, we have a range of natural yeast-based products such as nutritional yeasts (source of fiber and high-quality proteins), yeast with high content in mineral and vitamins and other yeast derivatives that are savory ingredients contributing to taste foundation in plant-based meals, whose palatability remains a factor that may be hindering its broader appeal.
Sustainability must be at the core of innovation: specialized ingredients can also be produced through fermentation; microorganisms can be used to convert various substrates to natural molecules and metabolites bringing an environmental advantage over the conventional chemical production, which is mainly powered by fossil fuels (4). By harnessing new technologies – including biotechnology- in the food systems, microorganisms can operate as efficient factories to produce affordable food ingredients contributing to a circular and bio-based economy while helping to reach sustainability goals by saving energy, reducing waste produced, water and land use, deforestation, and more.
10a)Indeed. A survey conducted by The International Alliance of Association (IADSA) in 2023 in more than 25 countries to assess preparedness of the supplement sector regarding environmental sustainability (6) revealed that, for more than 50% of the survey respondents, environmental sustainability is of high relevance to their company and that they UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) were taken into consideration . The most common UN SDGs that the companies are working towards are healthy and well-being (54% mention this) and responsible consumption and production (42%). Among the companies’ sustainability objectives, the most widespread goals are responsible marketing and labelling (86%) and ensuring food supplements that contribute to healthy and sustainable diets (86%).
In terms of products on the supplement market, we see a considerable amount of product launches with sustainability related claims on packaging. According to an Innova report (7), the most frequent messages used in a total of 1275 food supplements, are ethical (n582), good for the planet (n263) and made with sustainable ingredients (n70).
10b) According to Mintel, it is anticipated that, by 2030, consumers preferences will lean towards products that are nutritious, tasty, affordable, sustainable, and minimally processed (5). Consumers also pay more and more attention to sustainability messages on packaging. This clear trend towards transparency and verification is part of a broader consumer demand for clean and responsible products. Green claims are statements about the environmental benefit of products or services. When green claims are misleading or false, it is called greenwashing. Until very recently, the communication about the green nature of products has not been regulated and consumers have been facing a wealth of green claims which accuracy could not be verified. In March 2024, the EU adopted new rules on the environmental information to the consumers, banning greenwashing and unfair marketing practices and prohibiting dishonest practices such as the use of generic environmental claims without a proper substantiation. The so-called greenwashing Directive is intended to enable consumers to make informed purchasing choices based on reliable information about the sustainability of products. Companies will have to adopt a common methodology for substantiating green claims about the environmental footprint of their products and obtain a certification compliance from an independent verifier.
Sustainable sourcing
For example, our MenaQ7 Vitamin K2 as MK-7 is recognized for being clinically validated for bone health in children (1) and adults (2), and for cardiovascular health in adults (3,4). Last year, we introduced our new Palm-Free MCT Oil, which exemplifies our commitment to sustainability and quality. Our organically certified MCT Oil is derived exclusively from coconut sources. By making this conscious choice, we ensure we offer a more sustainable solution without compromising quality.
Sustainable processes
Another example is our newest ingredient offering, crafted by fermentation specifically to protect the native Rhodiola botanical species.
Found naturally in high altitudes in Europe and Asia and taking over 20 years to mature, the increasing demand for Rhodiola rosea became the main threat of overharvesting it. To ensure its sustainable harvest and trade, Rhodiola species were added to the CITES list of endangered species. Consequently, developing ecological ways to harness the benefits of Rhodiola has become a key step in preserving this species.
But we can still enjoy the benefits of this miraculous plant through an innovation in manufacturing: our fermentation process bypasses the need to harvest Rhodiola rosea, becoming CITES compliant by design.
Sustainable facilities
Finally, this commitment extends from our production processes to our facilities. Spawning from a desire to re-industrialize the Hainaut region in Northern France and a citizen commitment to rehabilitating a former industrial wasteland (Usinor), the upcoming Denain greenfield plant will create more than 100 jobs.
Our Denain plant will produce Gnosis's chondroitin, which will be unlike anything else currently available. Chondroitin is a recognized solution for reducing joint pain; however, 80% of the chondroitin in the market is manufactured in China, and 100% is produced from animal cartilage. Gnosis's Chondroitin will be produced using a natural fermentation process that is sustainable (bio-sourced in compliance with biodiversity), non-animal, and efficient (high purity and bioavailability).
The choice of the site is in line with the company's commitment: a desire not to artificially develop soils, along with the construction of a diverse 5.9-hectare compensation area for fauna and flora, creation of a 1.2-hectare nature reserve, and construction of habitats for various species.
In closing, human well-being depends on preserving the environment before anything else. This is why we transform microorganisms through natural processes like fermentation, acknowledging the fragility of our planet and striving to preserve it.
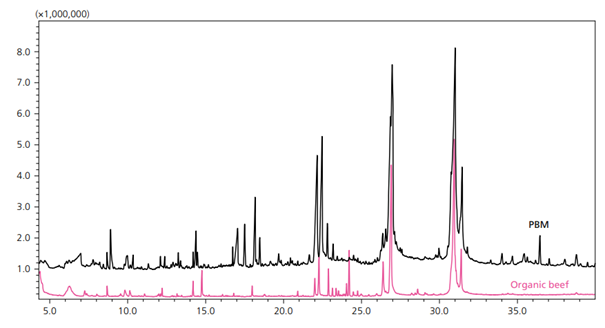
Figure 1. Overlaid Representative Chromatograms for PBM (black) and Organic Beef (pink) (6).
Panelists
References and notes
- International Health Conference, World Health Organization (WHO), 1948.
- WHO (2010) A healthy lifestyle - who recommendations, World Health Organization. Available at: https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/a-healthy-lifestyle---who-recommendations
- FMCG Gurus (2022), The route to Sustainability in 2022 - Global report
- Yup, L.S. (2016) Systems metabolic engineering turns microbes into factories, Scientific American. Available at: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/systems-metabolic-engineering-turns-microbes-into-factories/
- Mintel (2024) Plant-based report
- IADSA (2023) How the food supplement sector is embracing environmental sustainability. International Alliance of Dietary/Supplements Associations. United Kingdom.
- Innova Market Insight (2024) Sustainability report
Questions
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
How have consumer awareness & demands related to healthy lifestyle changed in the last 12 months?
Where do you see the greatest scientific achievement in nutritional sciences in the last 12 months?
Are there specific health benefit areas in which significant more clinical studies are being done than in others, comparing the last 3 years?
What are the key influencers driving consumer purchasing decision for supplements or health foods? Is substantiation of claims important?
How do consumer today judge their health status?
Please put the following parameter in order 1 highest priority 7 lowest priority:
- Physical Symptoms, like pain, fatigue, constipation, weight gain
- Fitness Levels: endurance, strength, flexibility,
- Health Tracking Devices and heart rate, sleep patterns, steps taken
- Diet and Nutrition: intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins.
- Mental and Emotional Well-being: stress levels, emotional balance, happiness
- Quality of sleep: Sleep quality and duration
- Medical Check-ups: blood pressure checks, cholesterol screenings, blood sugar tests
6.
Delivery formats can support consumer compliance and underline the technology driven approach of the brand.
a.
b.
c.
Do you see a consumer trend in preferences for certain delivery formats?
Are delivery format preference a regional, cultural aspect like taste?
Do you see a trend to carry out ingredient clinical trials using a selected delivery format as study product formulation or are most clinical studies still done in capsules?
7.
Consumer health concerns can vary widely across different regions and demographics globally. However, several common health concerns tend to be prevalent across various countries and populations due to globalization, lifestyle changes, environmental factors, and access to information.
a.
b.
Which are the key global consumer health concerns?
Do you see regional differences?
8.
There is a significant increase in the availability of apps and digital platforms focused on healthy lifestyle, particularly to support personalized approaches to mental wellbeing, metabolic support, weight management and physical fitness.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Do you see lifestyle apps as competition for supplement brands?
Do you think that these apps help to educate consumers, being more targeted when searching for supplements?
Did you consider setting up a lifestyle app to promote your supplement or your ingredient?
Did you set up a lifestyle app to promote your supplement/ ingredient and can you explore about your experience and business impact?
9.
AI (Artificial Intelligence) algorithms are today offered for various aspects of clinical trials to proof efficacy of your health ingredient or supplement.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Are consumers looking for substantiation of claims through AI driven clinical trials?
Did you consider working with an CRO specialist in AI to investigate your health ingredient or supplement?
If you applied already AI methods during the discovers/ development of your health ingredient, please share your experience and recommendation with us.
Do you think that in 2030 AI will be a manifest tool for clinical trials?
10.
A healthy lifestyle may also involve a commitment to sustainable practices for both personal and planetary health. This could include supporting ethical and environmentally conscious products.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
Do you agree that sustainability has become a growing concern also in the nutraceutical industry?
Are consumer looking proactively for brands which have ethical and environmental principles?
Are you looking for ethically sourced raw materials, ingredients?
Did you implement measures to establish resource-efficient processes?
Are you developing socially useful products and how do you define it?
11.
What are the major geographical differences related to healthy lifestyle trends?
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
What are the latest trends related to claims and product forms in China?
In the U.S.
In Mexico
How are claims and dosage forms differentiated in Europe? How does your company ensure compliance with health and safety regulations in Europe?
Do you have a country where you would like to speak about trends for products?
12.
Focus clinical studies. Overall, there has been a recognized push for more gender-inclusive, geographical, and target group focused clinical research. The same trend can be seen in clinical trials for supplements or functional foods.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Please select an area you are active in and let us know which is your hot topic ingredients for 2024 for this area, based on substantiated claim, parameters, biomarkers being studied and/ or clinical study being done. Please name ingredients by scientific name and composition and not by brand name.
Please select your geographical area:
Western (EU, USA)
Asia (China, Japan, Asia Pacific)
Americas (Middle and Latin America)
Kids development/ early life nutrition/infant in Western countries and AP
Adult nutrition and prevention of developing disease
Elderly nutrition and how to support quality of life during aging
Sports nutrition, within different life decades and activity levels
References and notes























