Panel discussion on...
Cognitive health
What are the latest global and regional trends in cognitive health supplements, and how do companies tailor their products to meet the unique needs of different markets?
M. A.: Consumers are increasingly incorporating diet and supplement changes to enhance focus, attention, and memory. While cognitive health was once a concern primarily for older individuals, younger consumers are now seeking brain-boosting ingredients like omega-3, iodine, choline, and nootropics.
In North America, mental well-being and stress management are major concerns, while in Europe, physical and mental well-being are equally valued (1). This shift is reflected in product launches like Bayer’s "Berocca Mind," introduced in September 2024, emphasizing mental wellness alongside physical health.
Traditionally, cognitive supplements targeted age-related decline and children's development, but companies now focus on enhancing cognitive performance for active individuals. For example, Unilever’s "Olly Brain Chews," launched in 2024, offers variations for focus, clarity under pressure, and energy.
Mushroom-based coffee alternatives are also gaining traction. SPINS (2) reported a 28% growth in mushroom-related cognitive health products in 2024. Notable launches include Bloomster’s "Feel Focused" and Thorne’s "Ginseng Plus," both leveraging lion’s mane for memory, concentration, and stress management. Digital-native brands like Spacegoods (UK) and MUD/WTR (USA) have achieved significant commercial success, with Spacegoods securing £2.5 million in seed funding and MUD/WTR reaching six-figure revenues within six months. While caffeine remains a key player in cognitive health, demand for caffeine-free alternatives is rising.
What are the most promising breakthroughs in cognitive health and/or supplements over the past year, and how are they influencing product development?
M. O.: Recent ingredient breakthroughs include growing interest in mushrooms and adaptogenic herbs, often formulated as coffee substitutes or beverages. Ingredients with demonstrated acute effects appeal to both younger consumers and older adults experiencing cognitive decline. These trends are driving innovation in product formats and broadening the target demographic.
How has the consumer understanding of brain health evolved recently, and what role do branded ingredients play in shaping their trust and preferences?
M. A.: Consumers of all ages recognize the link between brain health and overall well-being. They seek products addressing stress, sleep, mood, and cognitive function, shifting the perception of brain health from an aging-related issue to a lifelong concern.
The driving force behind consumers’ purchasing decisions is product efficacy, and they wish to see science-backed solutions (3). Through the use of branded ingredients, brands promote quality, clinical validation, and consumer trust by demonstrating proven efficacy and safety through rigorous research. The increasing popularity of these ingredients is reflected in several new product launches based on branded ingredients in the cognitive segment. For example, Cognivia, Cognigrape, Cognizin, Neumentix, BacoMind, Vitacholine, and Cereboost are appearing in products all over the globe.
How has the consumer understanding of brain health evolved recently, and what role do branded ingredients play in shaping their trust and preferences?
M. A.: Consumers of all ages recognize the link between brain health and overall well-being. They seek products addressing stress, sleep, mood, and cognitive function, shifting the perception of brain health from an aging-related issue to a lifelong concern.
The driving force behind consumers’ purchasing decisions is product efficacy, and they wish to see science-backed solutions (3). Through the use of branded ingredients, brands promote quality, clinical validation, and consumer trust by demonstrating proven efficacy and safety through rigorous research. The increasing popularity of these ingredients is reflected in several new product launches based on branded ingredients in the cognitive segment. For example, Cognivia, Cognigrape, Cognizin, Neumentix, BacoMind, Vitacholine, and Cereboost are appearing in products all over the globe.
Are there specific cognitive functions, such as memory, focus, or stress management, that are driving the majority of consumer interest? Why?
M. A.: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of mental well-being, and post-pandemic, stress remains a top concern. Over 40% of consumers define health as having low stress (4), stating mood and mental wellbeing are at the top of concerns they wish to address in the following months (5).Companies are responding with combination supplements addressing both stress and cognitive function. In 2024, Haleon (USA) launched "Centrum Clear Mind & Calm Mood," targeting stress relief and mental sharpness.
Daily struggles with mental energy, focus, and memory drive consumer interest in enhancing memory and alertness (6).E-sports, requiring high cognitive performance, have also contributed to this demand. Cellera Farmacêutica (Brazil) launched "Convivia" in 2024, addressing cognitive performance, focus, memory, and concentration.
What advancements in ingredient delivery systems are being made to enhance the bioavailability of cognitive health supplements?
M. O.: While advanced delivery systems are not yet widespread, progress has been made with extended-release caffeine, encapsulated herbal extracts, and liposomal formulations improving ingredient absorption, as seen in products like NooGandha (7).
How do you see the integration of AI and big data reshaping clinical trials for cognitive health ingredients and supplements?
M.O.: AI algorithms help companies analyze scientific literature, clinical trials, and consumer feedback to identify trends, optimize trials, and target specific subpopulations. AI also reduces costs by predicting outcomes and detecting subtle product efficacy differences.
However, one critical challenge lies in translating AI-detected improvements into meaningful benefits for consumers. If the effects are too subtle for users to perceive or associate with enhanced cognitive performance in their daily lives, the likelihood of repeat purchases diminishes, even if the data demonstrates a significant improvement. Balancing the precision of AI-driven insights with consumer-perceived benefits is therefore essential.
How do you see the integration of AI and big data reshaping clinical trials for cognitive health ingredients and supplements?
M.O.: AI algorithms help companies analyze scientific literature, clinical trials, and consumer feedback to identify trends, optimize trials, and target specific subpopulations. AI also reduces costs by predicting outcomes and detecting subtle product efficacy differences.
However, one critical challenge lies in translating AI-detected improvements into meaningful benefits for consumers. If the effects are too subtle for users to perceive or associate with enhanced cognitive performance in their daily lives, the likelihood of repeat purchases diminishes, even if the data demonstrates a significant improvement. Balancing the precision of AI-driven insights with consumer-perceived benefits is therefore essential.
What role does sustainability play in the cognitive health space, particularly in sourcing and manufacturing ingredients?
M.O.: Sustainability is shaping ingredient sourcing and manufacturing. Laboratory-grown herbal materials reduce reliance on traditional farming, minimizing environmental contamination. However, this method can be energy-intensive, requiring a balance between sustainability and efficiency.
Which emerging ingredients show the most potential for supporting cognitive health, and how are they being clinically validated?
M.O.: Emerging ingredients such as enXtra(8), Cognivia (9), and BrainBerry (10) demonstrate significant potential in supporting cognitive health. These are often derived from herbs, adaptogens, or fruit-based sources. Clinical validation is increasingly conducted using computerized cognitive testing batteries, which involve a combination of tasks designed to measure effects on various cognitive functions. These tests are now tailored specifically for nutrition products, enabling the detection of even subtle changes in cognitive performance. Studies also focus on both short-term (acute) effects and long-term outcomes over weeks or months.
Are there regional variations in consumer priorities for cognitive health supplements, such as stress relief in Asia versus memory enhancement in Western markets? How are these differences addressed in product development and marketing?
M.A.: Stress remains a major concern in Western markets, leading to product launches like Nu Skin’s (USA) "Feel Calm" and Bayer’s (Italy) "Supradyn" in 2024. The gut-brain connection is also gaining attention, as seen with GutPersonal’s (USA) "The Miracle Worker."
With rising life expectancy and declining fertility rates, aging populations in Asia-Pacific (11) present opportunities for cognitive health products targeting age-related decline. However, the cognitive market is globalizing and becoming more uniform among the regions, as Western markets adopt traditional Asian practices like the use of ayurvedic herbs (e.g. ashwagandha) or medicinal mushrooms.
How are regulatory landscapes across different regions influencing the claims and marketing of cognitive health supplements? What specific regulatory challenges should new entrants to this space be aware of?
M.O.: The regulatory landscape varies globally, complicating ingredient standardization. Differing lists of permitted ingredients, especially for herbal extracts and mushrooms, pose challenges. In Europe, a new safety assessment list may limit certain ingredients like ashwagandha, commonly used in cognitive formulations. Companies should navigate these evolving regulations carefully.
What innovative approaches are being used to educate consumers about the science behind cognitive health supplements?
M.A.: We are witnessing greater self-regulation in the health and wellness market, with brands actively promoting the science behind claims made on packaging. Fitness apps and generative AI, healthcare-related websites, celebrity or social media influences, and social media websites are most impactful on consumers’ treatment approach. This underscores the potential for the industry to employ a more tech-forward outreach strategy (4).
With increasing digital distractions, how can the supplement industry position itself to address the growing concern of digital fatigue and its cognitive impacts?
M.A.: While adaptogenic ingredients may improve our stress response, I believe likely the most effective countermeasure our industry can contribute to is to help foster a culture of limiting digital distractions. If I may allow myself a personal comment, I believe it is hard to expect any supplement’s effect to come close to simple measures such as switching off notifications for non-essential apps.
Do you see a shift towards multi-benefit supplements that combine cognitive support with other health areas, such as mood, energy, emotional well-being or immune function?
M.A.: Cognitive health supplements are increasingly positioned alongside other health benefits. Euromonitor identifies this as an appeal to consumers seeking a "magic pill" addressing multiple concerns. Examples include: Hypera’s (BRA) 2023 launch “Bifilac mind” – a probiotic positioned to help reduce feelings of stress and anxiety, contributes to improving memory, cognition, and attention, and helps with intestinal flora, immunity, and anti-inflammatory response. “Berocca Mind”, a 2024 launch by Bayer (AUS and NZL), positioned to enhance mental performance and improve mental endurance and alertness, so consumers can stay on top of what each day brings. Galinée's (FRA) 2024 launch “Calm & Microbiome”, targeting the intestine-brain-skin axis which is also claimed to help improve mood.
What are the main challenges and opportunities in differentiating cognitive health supplements from general wellness products in a crowded market?
M.A.: To differentiate cognitive supplements from general wellness products, brands should focus on specific cognitive needs like memory, focus, and attention. Educating consumers on the benefits of specific ingredients is also crucial. For example, consumers are unclear on the benefits of specific mushroom ingredients and parts of these ingredients (2). Clear communication on ingredient sourcing and functionality will help brands establish trust and stand out in the market.
Emerging evidence has also revealed the existence of the gut-brain axis - the bidirectional communication between the gut microbiome and the central nervous system – suggesting it may be involved in the progression of age-related cognitive impairment (12). However, it is still a question whether this can be manipulated to favorably influence cognitive and mental health outcomes.
How do differences in gender and age groups influence dosing strategies and health claims for cognitive health supplements? Are there specific considerations or opportunities for targeting these segments?
M.O.: Some sources suggest women are more prone to conditions such as depression (13) and anxiety (14) than men, providing an opportunity to target them with supplements with benefits for stress and mood management.
Younger demographics are more concerned about their mental health and stress levels. This provides an opportunity for brands with products positioned for stress, anxiety, calming effects, and so forth. Gen Z is also discovering neurohacking via podcasts and their social media feeds. This trend of discovering supplements through social media might suggest marketing strategies are becoming as important as product formulations.
“Baby boomers” are looking for solutions to address cognitive decline. 34% of senior consumers are concerned about losing mental agility (15). Brands that wish to target this demographic should, therefore, focus on developing supplements with claims that support memory and overall brain health.
More research is needed on dosing strategies, considering variations across demographics such as children, young adults, menopausal women, and seniors. Currently, few ingredients have age-specific dosage support. Advanced data processing tools can help tailor dosing strategies, similar to health claims, which depend heavily on regional regulations. In the EU, health claims require extensive and conclusive evidence, making approval processes particularly stringent.
Where do you see the cognitive health supplement market in the next 5 to 10 years, and what trends or innovations do you anticipate will define its future?
M.A.: I anticipate that well-defined and clinically proven effects of specific ingredients’ specific dosages on specific populations are a trend we will see even more of in the future. What I mean is that we will hopefully have clinical data on, for example, the exact effect of 500 mg of bacopa monnieri on post-menopausal women. Additionally, I expect that a key area of development will be excipients for enhancing organoleptic properties of finished products advancing to the level where we will be able to successfully mask any kind of bitter herb, typically found in cognition supplements, and will therefore enjoy a wider variety of deliver formats.
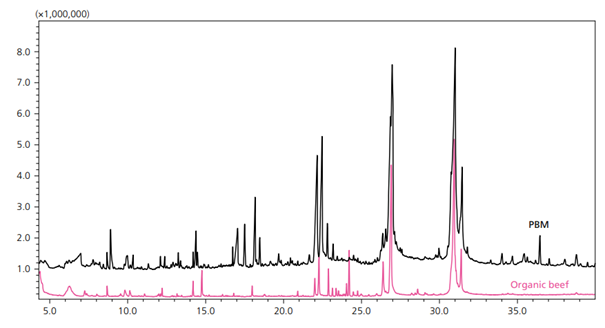
Figure 1. Overlaid Representative Chromatograms for PBM (black) and Organic Beef (pink) (6).
Panelists
References and notes
- STADA Health Report. 2024. Available at: https://www.stada-healthreport-2024.com/en
- SPINS data, in the 52 weeks ending Dec. 3, 2023.
- McKinsey Future of Wellness Survey. 2024. Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/consumer-packaged-goods/our-insights/the-trends-defining-the-1-point-8-trillion-dollar-global-wellness-market-in-2024
- Euromonitor International Health & Nutrition Survey. 2023.
- FMCG Gurus. Top Trend 8: For Today, Better Tomorrow. 2024.
- Kyowa Hakko. Survey of Cognitive Health Consumers. 2024.
- Xing D et al. Acute ashwagandha supplementation improves cognitive performance. JISSN 2020;17:67. Leonard et al. Acute and repeated ashwagandha supplementation improves markers of cognitive function and mood. Nutrients 2024; 16(12):1813. Remenapp A, Coyle K, Orange T, et al. Effectiveness of ashwagandha (withania somnifera) supplementation on adult’s cognition and mood. Journal of ayurveda and integrative medicine 2021. Available at: https://specnova.com/noogandha-research/
- Srivastava S, Mennemeier M, Chaudhary JA. A randomized placebo controlled clinical trial demonstrating safety & efficacy of enxtra in healthy adults. J Am Coll Nutr. 2021 Mar-Apr;40(3):224-236.
Srivastava, Shalini. Selective enhancement of focused attention by alpinia galanga in subjects with moderate caffeine consumption. Open Access Journal of Clinical Trials 2018. Volume 10. 43-49.
Srivastava S, Mennemeier M, Pimple S. Effect of alpinia galanga on mental alertness and sustained attention with or without caffeine: a randomized placebo-controlled study. J Am Coll Nutr. 2017 Nov-Dec;36(8):631-639.
Sivanandan, S. and Pimple, S. Molecular docking studies of alpinia galanga phytoconstituents for psychostimulant activity. Advances in Biological Chemistry 2018, 8, 69-80.
Srivastava, Shalini and Surekha R. Pimple. Effects of cymbopogon flexuosus, alpinia galanga , and glycyrrhiza glabra on attention: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. 2017. - Wightman et al. The acute and chronic cognitive effects of a sage extract: a randomized, placebo controlled study in healthy humans. Nutrients 2021, 13(1), 218.
Babault et al. Acute effects of salvia supplementation on cognitive function in athletes during a fatiguing cycling exercise: a randomized cross-over, placebo-controlled, and double-blind study. Front. Nutr., 2021 (8). - Ahles et al. The effect of long-term aronia melanocarpa extract supplementation on cognitive performance, mood and vascular function: a randomized controlled trial in healthy, middle-aged individuals. Nutrients 2020 Aug 17;12(8):2475. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7468716/
- Euromonitor International. Spotlight on Asia Health and Beauty Consumers. 2024.
- Liang et al. Gut microbiome, cognitive function and brain structure: a multi-omics integration analysis. Open Access Translational Neurodegeneration 2022 (11);49. Available at: https://translationalneurodegeneration.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40035-022-00323-z
- Salk R. H., Hyde J. S., Abramson L. Y. Gender differences in depression in representative national simples: meta-analyses of diagnoses and symptoms. Psychol Bull 2017 Apr 27;143(8):783-822. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5532074/
- McLean C. P., Asnaani A., Litz B. G., Hofmann S. G. Gender differences in anxiety disorders: Prevalence, course of illness, comorbidity and burden of illness. J Psychiatr Res 2011 Mar 25;45(8):1027-1035. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3135672
- IQVIA. Unlocking Opportunities in the Healthy Aging MarketWebinar. 2024. Available at: https://www.iqvia.com/events/2024/06/unlocking-opportunities-in-the-healthy-aging-market